Understanding Email Policies of Google and Microsoft: Spam Detection and Circumvention Methods
In the digital age, email remains a primary mode of communication for both personal and professional interactions. However, with the convenience of email comes the persistent threat of spam, phishing, and other malicious activities. Major email service providers like Google and Microsoft have implemented sophisticated spam detection systems to protect their users. This article delves into the email policies of Google and Microsoft, focusing on spam detection mechanisms and potential methods to circumvent these filters.
Google’s Email Policies: Spam Detection Mechanisms
Gmail, a service provided by Google, employs advanced spam detection techniques that leverage artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. The primary goal is to protect users from unwanted emails while ensuring legitimate communications reach their inboxes.
How Gmail’s Spam Filters Work
Gmail’s spam filters analyze various signals to determine whether an email is spam. These include:
- User Feedback: Gmail learns from user interactions, such as when users mark emails as spam or move them to the inbox. This feedback helps refine the filter’s accuracy over time.
- Email Characteristics: Factors such as the sender’s IP address, domain reputation, and whether the sender is authenticated significantly influence spam detection.
- Content Analysis: The content of the email itself is scrutinized for common spam indicators, including specific keywords or phrases often associated with spam.
- Bulk Sender Authentication: For bulk senders sending over 5,000 messages daily, Gmail has introduced stricter regulations requiring email authentication to confirm sender identity. This includes using protocols like SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) to validate the source of emails
Spam Filter Customization
Gmail allows administrators to customize spam settings through the Admin console. This includes creating approved sender lists that can bypass spam filters. By whitelisting certain email addresses or domains, organizations can ensure important communications are not inadvertently marked as spam.
Microsoft’s Email Policies: Spam Detection Mechanisms
Microsoft’s email service, particularly through Outlook and Exchange Online, also employs robust spam detection strategies aimed at safeguarding user inboxes.
How Microsoft’s Spam Filters Work
Microsoft utilizes a combination of machine learning algorithms and user-defined policies to filter out unwanted emails. Key aspects include:
- Quarantine Policies: High-confidence spam messages are typically quarantined rather than deleted outright. This allows users to review potentially important emails that may have been misclassified.
- User Customization: Similar to Gmail, Microsoft allows users to set specific rules regarding how suspected spam should be handled. Users can choose whether to move such emails to junk folders or quarantine them for review.
- Zero-Hour Auto Purge (ZAP): This feature enables automatic removal of malicious emails shortly after they are identified as threats, minimizing exposure risk for users
How Microsoft’s Spam Filters Work
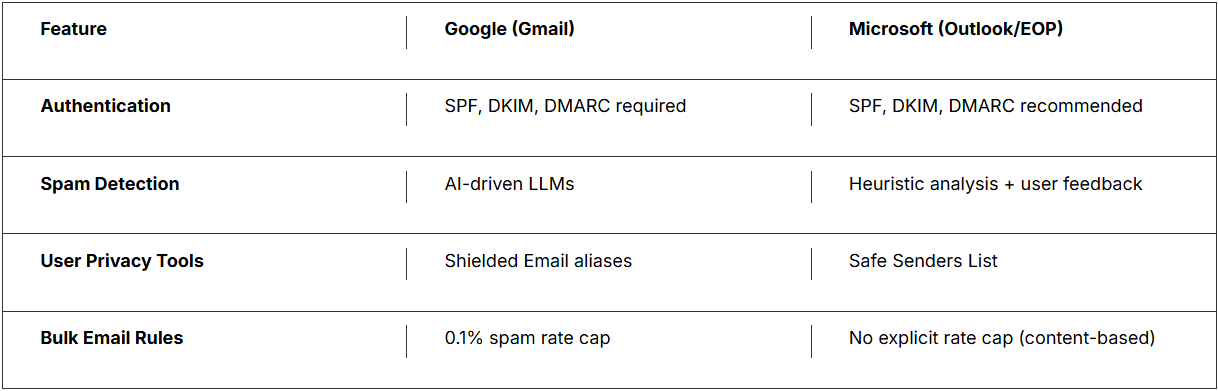
Feature
Google (Gmail)
Microsoft (Outlook/EOP)
Authentication
SPF, DKIM, DMARC required
SPF, DKIM, DMARC recommended
Spam Detection
AI-driven LLMs
Heuristic analysis + user feedback
User Privacy Tools
Shielded Email aliases
Safe Senders List
Bulk Email Rules
0.1% spam rate cap
No explicit rate cap (content-based)
Spam Filter Configuration
Administrators can configure various settings in Microsoft Defender to enhance spam protection. This includes adjusting actions taken on detected spam and ensuring that bulk complaint levels are monitored effectively
Circumventing Spam Filters: Techniques and Strategies
Despite the robust measures employed by Google and Microsoft, some individuals attempt to bypass these spam filters for malicious purposes. Understanding these methods can help organizations better defend against such tactics.
Common Techniques Used to Bypass Spam Filters
- Using Legitimate Email Templates: One common strategy involves copying legitimate emails that have previously bypassed filters. By mimicking the structure and language of these emails, attackers may increase their chances of success.
- Personalized Messaging: Crafting personalized messages that target specific individuals rather than generic mass emails can evade detection. Personalization reduces the likelihood of triggering spam filters that often flag bulk communications as suspicious.
- Exploiting Misconfigured Servers: Attackers sometimes take advantage of organizations with poorly configured mail servers or outdated content filters that allow direct delivery of malicious emails without scrutiny.
- Whitelisting Approved Senders: Some attackers may attempt to get their domains whitelisted within an organization’s email settings by posing as legitimate entities or exploiting existing relationships.
- Dynamic Sending Patterns: Maintaining variability in sending patterns—such as altering the timing between sent emails—can help avoid detection by filters that monitor for high-volume sending behavior typical of spammers.
Best Practices for Organizations
To mitigate risks associated with potential circumvention tactics, organizations should adopt several best practices:
- Implement Strong Authentication Protocols: Ensure all outgoing emails are authenticated using SPF, DKIM, and DMARC protocols to enhance deliverability and reduce spoofing risks.
- Regularly Update Spam Policies: Continuously review and update email policies based on emerging threats and changes in user behavior.
- Educate Users: Train employees on recognizing phishing attempts and suspicious emails to reduce the likelihood of falling victim to attacks that bypass technical defenses.
- Utilize Advanced Filtering Solutions: Consider additional security layers beyond built-in filters provided by Google or Microsoft, such as third-party email security solutions that offer enhanced threat detection capabilities.
- Monitor Email Analytics: Use tools provided by Google Postmaster Tools or Microsoft Defender to analyze domain health and monitor email performance metrics regularly.
In conclusion, while Google and Microsoft have established comprehensive policies aimed at detecting and mitigating spam threats effectively, there remains a continuous battle against those who seek to exploit vulnerabilities in these systems. By understanding both the mechanisms employed by these platforms and the methods used by malicious actors, organizations can better protect themselves against unwanted intrusions into their digital communications.
Sources
- https://clean.email/gmail-spam-filter
- https://knowledge.workspace.google.com/kb/how-to-bypass-the-spam-filter-for-incoming-emails-000006661
- https://blog.admindroid.com/increase-microsoft-secure-score-with-essential-spam-protection-settings/
- https://blog.clickpointsoftware.com/gmails-sender-requirements
- https://mailtrap.io/blog/avoid-spam-filters/
- https://shrparesearch.peoplemattersglobal.com/?refid=webbanner_anz
- https://anz.peoplemattersglobal.com/article/technology/why-gmails-2025-upgrade-might-mean-its-time-for-a-fresh-email-address-43831
- https://mailtrap.io/blog/outlook-spam-filter/
- https://www.nakivo.com/blog/configuring-office-365-spam-filter/
- https://posts.specterops.io/fly-phishing-7d4fb56ac325
- https://www.saleshandy.com/blog/avoid-spam-filters/

